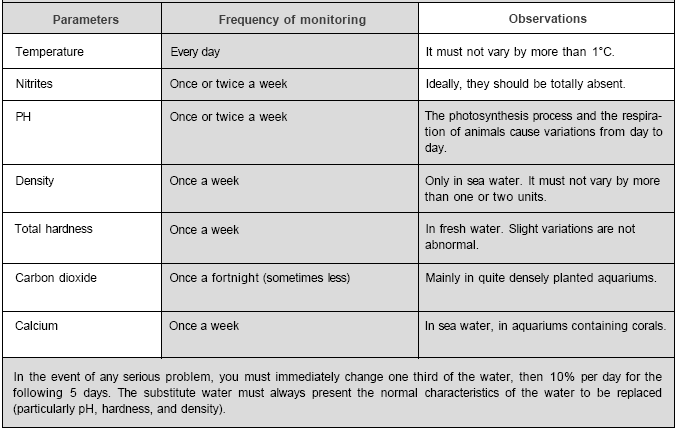
CHANGING THE WATER
Partial water changes, at regular intervals, are one of the keys to success in
fishkeeping. The combination of this operation with siphoning eliminates both assorted
detritus and some of the nitrates which eventually accumulate.
The clear water that is introduced supplies some mineral elements and provides
a stimulus for the aquarium: the growth of fish, the triggering of egg-laying, and
the growth of plants.
After 2 months or so you will see a striking contrast with aquariums in which
the water has not been renewed. A change of 5-10% of the volume per week is therefore
recommended. This obviously demands a stock of water with identical characteristics
to that of the aquarium (especially pH, hardness, and salinity).
PARAMETERS TO BE MONITORED
The ideal solution is daily renewal of a small amount, with the help of a drip
(see page 256). This technique is becoming more common among experienced aquarists.
It requires a special installation, and above all an overflow for the aquarium -
equipment which is not readily available in every case.
However, many fishkeepers find this system the ideal solution:
- the maintenance is reduced, as the water changes are less frequent;
- there are no abrupt variations in the environment;
- various substances, such as nitrates, are regularly eliminated and therefore
do not accumulate;
- it entails a regular, though limited, supply of the various substances contained
in the water (mineral salts, trace elements);
- the pH is stabilized;
- this method seems to restrict the growth of certain somewhat unsightly algae.
A word of wisdom: the water siphoned off a freshwater aquarium is excellent for
watering house plants as it contains dissolved organic matter!
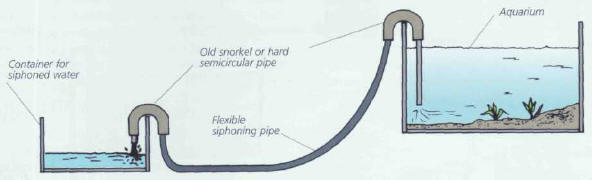
A TRICK FOR SIPHONING OFF WASTE
People who live with aquarists dread siphoning time, as it often leads to floods!
The pipes can be too flexible, with a tendency to slip out of the aquarium or the
container for the siphoned water.
The trick is to get hold of a washing machine draining pipe or a snorkel, and
slide the siphoning pipe inside it, making it possible to bend it over the side
of the container or tank. A stiff bent pipe can also be used to siphon in the less
accessible parts of an aquarium (grottoes, for example).
|