EVAPORATION AND THE WATER LEVEL
The water in an aquarium evaporates.
This has no ecological consequences, but it does mean that the surface of the
water comes into view at the top of the panes, which is hardly attractive. This
must therefore be adjusted on a regular basis, usually at the same time as you make
a partial water change.

When stemmed plants grow too big, you can consider taking
cuttings.
After a while a regular increase in the hardness of fresh water (or the salinity
of sea water) is noticeable: the water that evaporates from the surface is fresh
water containing no salts, even in sea water, and so there is a progressive concentration
of salt or other mineral substances in the aquarium.
To avoid this problem, replace the evaporated water with very soft or demineralized
water in order to readjust the hardness or density. This can be done when you change
the water, by slightly diluting the new water with fresh water. Readjustment of
the water level is not necessary if you are using a drip that functions automatically.
A SIMPLE DRIP TECHNIQUE
Two points must be taken into account: the arrival of the new water and the overflow
of the aquarium water.
Do-it-yourself experts may consider making a connection with the plumbing pipes
in the home, but there is a more simple solution. Take a PVC container, such as
a jerry can with a faucet, for use above the water level of the tank. For aesthetic
reasons, this is hidden in a cupboard or other piece of furniture. A flexible PVC
pipe can be used to connect the faucet with the aquarium.
Water from the aquarium can flow into another container, larger than the first,
to avoid any risks of overflowing (diagram 1).
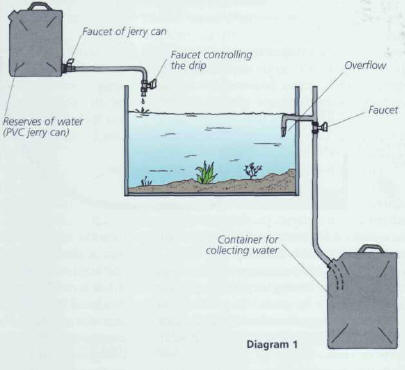
There remains the problem of the aquarium overflow. You can get a glass store
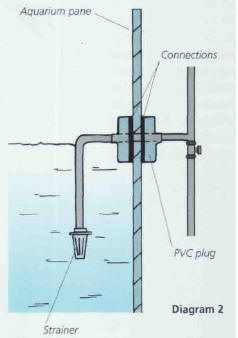
to make a hole in a side or rear pane when you are mounting or buying the tank.
Insert a PVC plug with connections for the evacuation pipe; do not forget to also
provide an escape for the water (diagram 2).
There is another solution: use a siphon that functions continuously (diagram
3). The water level can be regulated by raising or lowering loop A, and a small
diameter (1 cm) ensures the continuity of the operation.
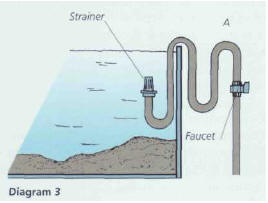
This device can easily be attached to the inside and outside of the aquarium
with suction pads. It is best not to put a diffuser near the entry of the siphon,
as there is a danger that bubbles may interfere with its functioning. Always put
a strainer on the end to avoid any small fish or large pieces of debris from getting
sucked up and causing a blockage. The system is set in motion by sucking on the
pipe. You will have to adjust the drip by trial and error, after calculating the
volume that needs to be renewed (around 1 % of the volume of the aquarium per day).
Maintaining the vegetation
When you are siphoning on the bed, you must remove any dead leaves that may have
fallen. Likewise, cut off, with a razor blade or scissors, any leaves that are starting
to rot.
When the plants need a new lease of life, you can take cuttings or use another
means of vegetative multiplication.
Liquid or solid fertilizer should be added regularly; the instructions on the
pack will tell you how often and at what rate each product needs to be added.
|